NCERT-GEOGRAPHY-CLASS-07-CHAPTER-04
👉 First Study These chapters 👀
👉NCERT-GEOGRAPHY-CLASS-07-LINK-PAGE 👀
What is Air?
- A mixture of various gases, we find on the earth is air.
Composition of the atmosphere
👉 इजरायल फिलिस्तीन विवाद- कारण-भाग-2 👀
- A huge mass of air as a blanket we find around the earth is known as the atmosphere.
- In the composition of the atmosphere we have
01- nitrogen 78%,
02- oxygen 21%,
03- carbon dioxide 0.36 per cent and
04- rest of the gases including ozone hydrogen-helium Neon.
Gases we inhale?
- The gases we inhale are,
- a large amount of oxygen
- a little bit of nitrogen.
The mechanism through which plants intake "Nitrogen"
- Plants do not intake directly nitrogen but through bacteria which are found in the soil and roots of a plant.
- This bacteria is a microorganism that transforms atmospheric nitrogen into fixed nitrogen which is the inorganic compound usable by plants.
What is air circulation?
👉 UPSC-GEOGRAPHY+EVS MAINS ANSWER WRITING 👀
- In the atmosphere of a particular place, we have the heating and the cooling of air.
- When the air gets heated up it becomes lighter and starts to expand and goes up.
- On the other hand cold air which sinks down fills up the place vacated by rising hot air.
- It is an ongoing process and that's how the heated air and cold air change their respective places simultaneously known as Air Circulation.
👉 अन्य विषय की अध्ययन सामग्री के लिए साइटमैप देखें 👀
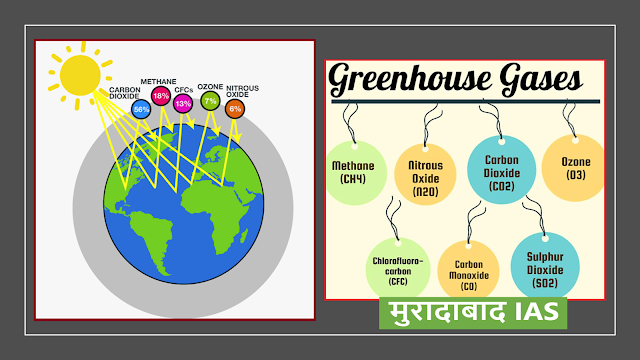
The utility of carbon dioxide
- The main task of carbon dioxide is to trap the heat radiated by the earth's surface.
- The plant Kingdom uses carbon dioxide to make their food and as a by-product releases oxygen.
- On the other hand, the Animal Kingdom and human beings inhale oxygen and release carbon dioxide as a by-product.
- That's how a perfect balance is maintained in the earth's atmosphere.
- Burning fossil fuels more than the proportional requirement results in the addition of more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- As a result, that atmosphere traps more terrestrial radiation causing the increment of average atmosphere temperature known as global warming.
इजरायल फिलिस्तीन विवाद- कारण-भाग-3
Which is a greenhouse gas
- Carbon dioxide gas is a greenhouse gas.
layers of the Earth's Atmosphere
👉 For OTHER SUBJECTS study click on SITEMAP 👀
Ozone layer
- We found the ozone layer in the second atmospheric layer of the earth which is the "stratosphere".
- The main task of the ozone layer is to absorb ultraviolet radiation from the Sun.
Ionosphere
- The ionized zone of the Earth's upper atmosphere, which we find in the thermosphere.
What is temperature
- The measuring of the degree of the hotness or coldness of a given place is known as the temperature of that place.
- Variation in the temperature is subjected to
01- latitudinal position,
02- degree of insulation,
03- location, and
04- relief feature.
Insolation
- The incoming solar energy is the hotness from the Sun which is coming to the Earth's surface and is intercepted by the Earth known as insolation.
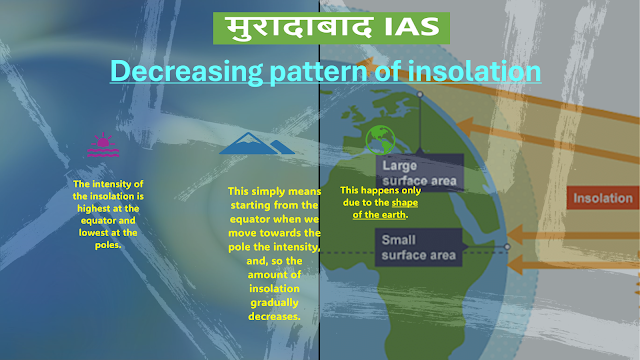
Decreasing pattern of insolation
- The intensity of the insolation is highest at the equator and lowest at the poles.
- This simply means starting from the equator when we move towards the pole the intensity, and, so the amount of insolation gradually decreases.
- This happens only due to the shape of the earth.
Why the temperature of the city is higher (Heat Island) than a village
- A city is a compact unit whereas a village is a much open unit.
- The city has material in quantity, the material which is more prone to intercept solar insolation.
- On the other hand in the village, this amount is less in quantity.
The atmosphere of the moon
- On the moon, you don't have the atmosphere just because the moon is not having that required amount of gravitational pull we have on the earth.
Air pressure
- The exerted pressure weight of air on a given unit place of the earth is known as air pressure.
Distribution of air pressure
- As we move up in the atmosphere, in a proportional manner, the air pressure starts to reduce.
- Air pressure is highest at the sea level/ sea surface.
- The temperature of a given place -&- its latitude position are major factors that determine the air pressure of a given place.
Low-pressure area
- In the presence of high-temperature air becomes lighter and starts to lift up creating a low-pressure area.
- The low-pressure area of a given place is characterized by cloudy weather and moist air.
Wind
- The
01- the horizontal movement of air,
02- from a high-pressure zone towards a low-pressure zone,
03- in a particular direction known as wind.
Types of winds
01-Permanent winds - Equatorial winds are their example
02-seasonal winds - The south-West monsoon of India is the classic example
and
03-Local winds - Loo which blows during the May and June months is an example of local wind.
Land breeze and sea breeze
- When the wind blows from the sea toward the land known as the sea breeze and the opposite of it is known as a land breeze.
- The sea breeze blows during the daytime why does the land breeze blow during the nighttime.
Moisture
- Through the process of evaporation, the transformation of water into two vapours is known as moisture.
Humidity
- At a given place and time the amount of moisture present in the air is known as humidity.
- When the humidity is less than a hundred per cent we called as relative humidity
Humid day
- On a humid day, the air is full of water vapour that's why cannot hold water vapour.
- That's why we are sweating all day when it is a humid day.
Clouds?
- The rising water vapour, simultaneously, starts to cool down
- causing the process of condensation which transforms water vapour into water droplets.
- The mass of that water droplet is known as a cloud.
Precipitation
- A cloud has a relative capacity to hold water droplets.
- When the cloud loses its holding capacity and the droplets start to come down the process is known as precipitation.
Rain
- When the precipitation comes to the Earth's surface in the form of water droplets known as rain.
Types of rainfall
- We have three kinds of rainfall one is
01-Convectional rainfall,
02-Orographic rainfall and
03-Cyclonic rainfall.
👉 मणिपुर,
नव साम्राज्यवाद (New Colonialism ) एवं AFSPA-भाग-02 👀
🙏🙏.....
















Comments