NCERT-GEOGRAPHY-CLASS-07-CHAPTER-03-LANDSFORMS
👉 Study This Also 👀
Lithosphere
- The lithosphere is the combination of the earth
- Crust, and
- the solid upper portion of the mantle.
- It simply means the combined joint portion of the crust and the solid copper belt of the mantle known as the lithosphere.
Lithospheric plates
- The breakaway portion of the lithosphere is known as the lithospheric plates.
- We have 7 major and around 15 minor plates.
👉 For OTHER SUBJECTS study click on SITEMAP 👀
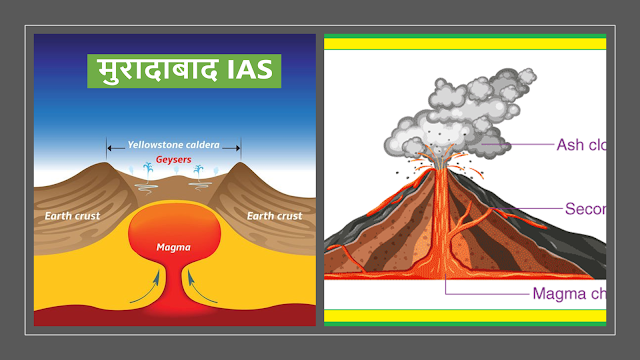
Magma & Volcano
- Molten or semi-molten
material, which, in its mixture, has molten
rocks, gases, and water vapor is known as magma.
- It is formed in the mental motion of the earth, as, it is a product of heat and pressure.
- The route through which Magma comes on the earth's surface is known as a vent.
- When the molten magma erupts, from the Earth's surface, through a vent known as a "volcano."
Tectonic Movement
The lithospheric plates are not static, but, always in a continuous movement is known as a tectonic movement.
👉 UPSC-GEOGRAPHY+EVS MAINS ANSWER WRITING 👀
Endogenetic forces
- The tectonic movement in the interior of the place is caused by the movement of magma inside the earth, in a circular path, known as "convective currents".
- The same movement of magma that causes forces to act from inside is known as endogenetic forces.
- These include -
- Earthquake,
- Volcano,
- Landslides,
- mountain building.
Exogenetic forces
- The forces which act on the surface of the earth are known as exogenic forces.
- The exogenic forces are-
- River,
- Wind,
- sea waves, and
- glaciers.
Earthquakes
- Due to the tectonic movement when there is a vibration on the surface of the earth all-around this vibration is known as an earthquake.
Focus
- A point inside the crust of Earth from where the earthquake waves started.
Epicenter
- The point above the Earth's surface is vertical to the focus known as the epicenter.
- Earthquake vibrations travel outward from the epicenter known as earthquake waves.
Types of earthquake waves
- We have 02 kinds and four types of earthquake waves that are-
- longitudinal P waves,
- S wave is a transverse wave, categorized as a "body wave".
- "L" -&- "R" waves are categorized as surface waves.
👉 UPSC मुख्य परीक्षा उत्तर लेखन 👀
Seismograph
- An instrument through which an earthquake is measured.
Weathering
- The natural process
through which the wearing and tearing down
(sedimentation) of the Earth's surface
got started.
Through this process,
rocks break into sediments.
Erosion
- Taking away that weathering material (sediments) through the different natural agents is known as erosion.
Waterfall
- When is a stream of water tumbling down over a hard Rock surface or down a steep valley side known as a waterfall?
Jog Falls was created by the Sharavati River dropping 253 m (830 ft).
It is the third-highest waterfall in India after the Nohkalikai Falls with a drop of 335 m (1,099 ft) in Meghalaya, is fed by the rain and is located on the edge of the "Cherrapunji Plateau."
The second highest fall is Dudhsagar Falls with a drop of 310 m (1,020 ft) in Indian state, Goa.
Meanders
- When the river enters the plain, its flowing causes it to twist and turn, so this large twist and turn is known as a meander.
- The point here to note is it is a feature of the plain area.
Oxbow lake
- In a gradual process,
- at the banks of the meander erosion and deposition process started,
- which causes the loops of the meander to cut off from the river.
- As a product, separate water bodies formed along the bank of the river, known as an oxbow lake.
Floodplains
- When the river stream is overflowing,
- the water breaks the bank of the river (Natural Levees), and
- enters the nearby area in the form of a flood.
- As floodwater tends to stay in the flooded area
- it deposits its sediments, which is a layer of fine soil, over there,
- it leads to the formation of a plain area known as flood plains.
Levees
- In the deposition process,
- due to the depositional activities when the banks of the river raised because of sediments, silt, and other material
- are pushed aside by the flowing river called levees.
Distributaries
- Due to the lower gradient of a slope or almost negligible slope gradient,
- in addition to heavy sediment loads,
- the main river stream breaks into the various streams known as distributaries.
Delta
- In the process of formation of distributaries, along with the sedimentation activity, regions form near the river mouth known as the "delta".
Waves
- When there is friction between the wind & water body surface water leads to continuous disturbance which causes waves in the water body.
Sea caves
- Sea waves, along the sea coast, give rise to the coastal landforms through the process of erosion and deposition.
- This process, when the sea wave continuously hit a rock, led to the formation of a hollow cave, known as a sea cave.
Sea arches
- With the continuous hitting on the sea caves
- by sea /ocean waves,
- with time, now opening done to another hand
- which means now the roof, with support of stacks, is known as sea arches.
Stacks
- When the roof of sea arches also diminished and only the walls are there known as.
Sea Cliff
- On the coast, due to the continuous erosion by sea waves, rises vertically against waves propagation known as a sea Cliff.
Beaches
- As sea waves,
- through the process of backwash deposit sediments along the shore
- a new kind of landform forms known as a beach.
👉 मणिपुर, नव साम्राज्यवाद (New Colonialism ) एवं AFSPA-भाग-01 👀
River of ice
- The glaciers are known
as the river of
ice.
- This we have studied earlier chapters also.
Glacier
moraines
- In glacier movement -
- when the big size and small size rocks,
- sand, and
- silt is carried away with the ice and gets deposited
- then these deposits are known as glacier moraines.
Mushroom rocks
- In the desert area when we see a mountain of sand in the shape of a mushroom known as a mushroom rock.
- As a special feature of desert areas, the shape of these mushroom rocks is the work of wind through the process of erosion.
- In desert areas wind erodes the lower section or the lower part of the Rock more than the upper section, as a result, the rocks take the form of mushroom-like.
Sand dunes
- A low hill-like structure in the desert area
- It is the outcome of the product of deposit channel activities of the wind known as sand dunes.
👉 Upcoming CHAPTERS 👀
Loess
- In the wind deposition process, the deposition of clay over a large area is known as loess.
🙏🙏.....
👉 इंदिरा गांधी / INDIRA
GANDHI- भारतीय राजनीति का
अध्याय 👀



























Comments